Note
Click here to download the full example code
Chaining functions together#
This example demonstrates chaining multiple functions together.
Out:
calling func_a
calling func_b
calling func_c
<Container (func_a: NoneType, func_b: NoneType, func_c: NoneType)>
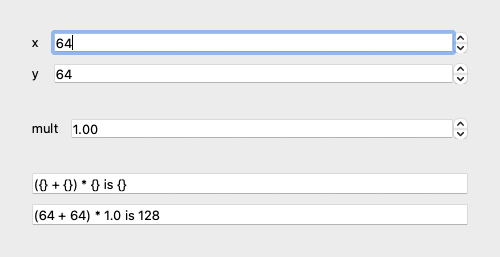
from magicgui import magicgui, widgets
@magicgui(auto_call=True)
def func_a(x: int = 64, y: int = 64):
"""Callable function A."""
print("calling func_a")
return x + y
@magicgui(auto_call=True, input={"visible": False, "label": " ", "max": 100000})
def func_b(input: int, mult=1.0):
"""Callable function B."""
print("calling func_b")
result = input * mult
# since these function defs live in globals(), you can update them directly
func_c.input.value = result
return result
# alternatively, you can the `widget.called` signal to connect a callback function
# where the result of the function being called is at `value`
@func_a.called.connect
def _on_func_a(value: str):
func_b.input.value = value
@magicgui(
auto_call=True,
input={"visible": False, "max": 100000},
result_widget=True,
labels=False,
)
def func_c(input: int, format: str = "({} + {}) * {} is {}") -> str:
"""Callable function C."""
print("calling func_c\n")
return format.format(func_a.x.value, func_a.y.value, func_b.mult.value, input)
container = widgets.Container(
widgets=[func_a, func_b, func_c], layout="vertical", labels=False
)
container.native.setMinimumWidth(500)
func_a()
container.show(run=True)
# notice which functions get called when you change each widget.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.041 seconds)
Download Python source code: chaining.py